Wholesale Price Index (WPI): Meaning, Calculation, and Key Differences with CPI
Syllabus: Indian Economy (UPSC Prelms, GS III)
What is the Wholesale Price Index (WPI)?
The Wholesale Price Index (WPI) measures changes in the prices of goods sold in bulk at the wholesale level, i.e., from businesses to other businesses. It acts as an important indicator of supply–demand trends, production costs, and inflation pressure in the economy.
WPI in India is calculated and released monthly by the Office of the Economic Adviser, Ministry of Commerce & Industry. The index reflects the average price level for the entire month, not just a specific day.
A rise in WPI indicates wholesale inflation, while a fall signals easing price pressures.
Why is WPI Important?
- Helps track supply-side inflation, especially in manufacturing and primary goods.
- Useful for industries to plan production, procurement, and pricing decisions.
- Provides early signals of inflation before they appear in retail markets.
- Often used by analysts to study trends in industry, manufacturing and construction.
Though important, WPI is no longer used by the RBI for monetary policy decisions. The RBI now uses CPI (Consumer Price Index) as the main inflation indicator.
WPI vs CPI: Key Differences
| Feature | WPI | CPI |
|---|---|---|
| Measures | Wholesale prices of goods | Retail prices of goods and services |
| Covers | Only goods | Goods + Services |
| Used by RBI? | ❌ No | ✅ Yes, CPI guides monetary policy |
| Focus | Producer/wholesale inflation | Consumer inflation / cost of living |
CPI reflects the price burden on consumers, while WPI captures inflation trends earlier in the supply chain.
Current WPI Series (Base Year 2011–12)
To align WPI with GDP and IIP, the base year was updated from 2004–05 to 2011–12.
The new series (effective April 2017) tracks the prices of 697 commodities, classified into:
- Primary Articles – 22.62%
(Food articles, crude petroleum, minerals) - Fuel and Power – 13.15%
(Coal, electricity, mineral oils) - Manufactured Products – 64.23%
(Food products, chemicals, textiles, metals, machinery)
How is WPI Calculated?
WPI is a weighted average of the prices of selected goods:
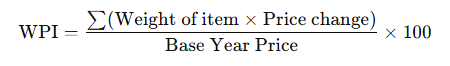
Each item’s weight depends on its share in total wholesale trade value.
In Summary
The Wholesale Price Index remains a crucial indicator for understanding producer-level inflation and supply conditions in India. While the RBI relies on CPI for policy decisions, WPI continues to provide valuable insights into production costs, commodity cycles, and industry-level inflation trends, making it important for UPSC aspirants, policymakers, and businesses.











