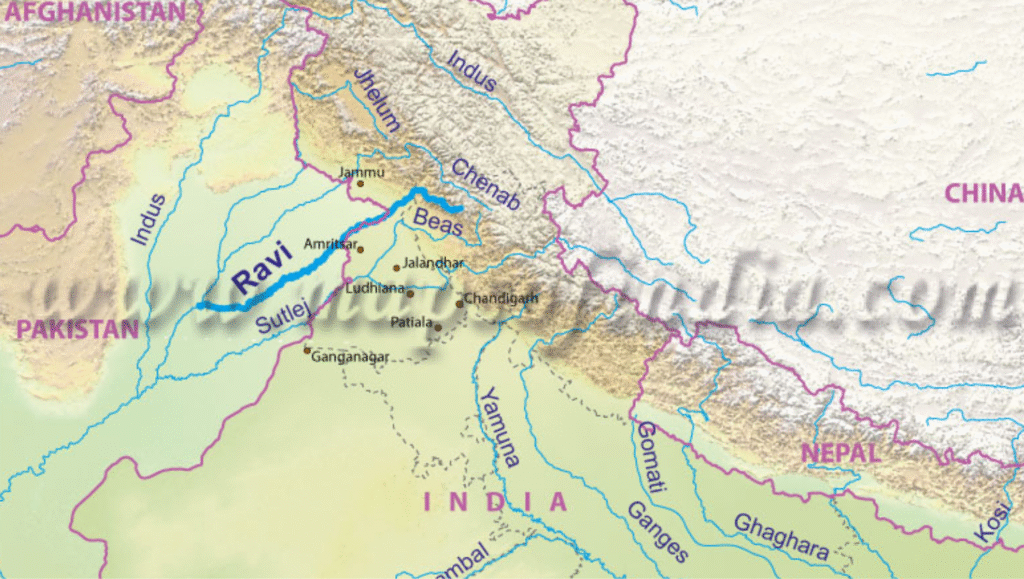
Ravi River
Syllabus: Geography (UPSC Prelims)
Source: TH
Context:
Floodwaters from the Ravi River recently submerged the Kartarpur Corridor complex in Pakistan’s Narowal district, including Gurdwara Darbar Sahib. Over 100 people were stranded, prompting large-scale evacuations.
Location & Basin
- One of the three eastern rivers of the Indus Basin, allocated to India under the Indus Waters Treaty (1960).
- Flows through Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Jammu & Kashmir (India) and into Punjab (Pakistan) before merging with the Chenab.
Source & Course
- Origin: Bara Bhangal in the Chamba region, Himachal Pradesh.
- Flows through deep Himalayan gorges, then into Punjab plains via Madhopur.
- Forms a short India–Pakistan boundary stretch, enters Pakistan near Narowal, passes Shahdara (Lahore), and joins the Chenab near Ahmadpur Sial.
Tributaries
- Right bank: Budhil, Baira, Siul.
- Left bank: Ujh (J&K), Basantar, Sewa.
Major Infrastructure in India
- Ranjit Sagar (Thein) Dam – irrigation + hydropower.
- Shahpur Kandi Project – downstream storage & irrigation.
- Madhopur Headworks – supplies the Upper Bari Doab Canal (UBDC).
- Chamera Hydropower Projects (Himachal Pradesh).
- Proposed Ujh Multipurpose Project (J&K).
Physiography & Soil
- Upper course: Narrow gorges in Himalayas.
- Lower course: Fertile alluvial plains (Punjab Doabs).
- Soils: Alluvial (plains), savanna and ferrallitic (sub-mountain tracts).
Climate & Hydrology
- Snowmelt + monsoon-fed river.
- Seasonal floods common in Pakistan Punjab (Narowal, Shahdara, Lahore).
- Peak flow: July–September (monsoon).
Economic & Cultural Importance
- Key source of irrigation in Punjab’s Doab region.
- Important for hydropower (Chamera, Thein projects).
- Religious significance: Gurdwara Darbar Sahib (Kartarpur) and other Sikh heritage sites.