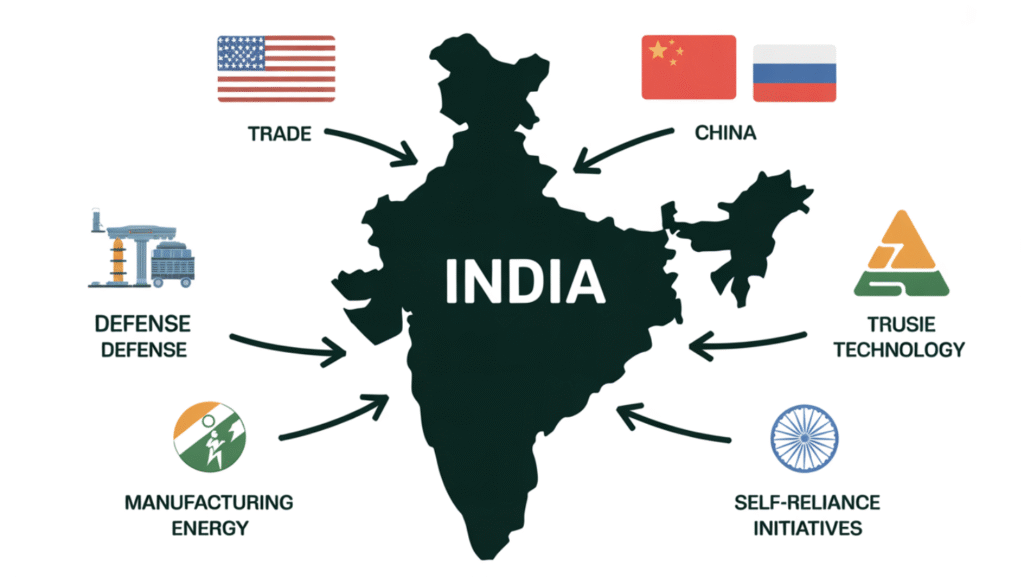
India’s Dependence on Foreign Nations
Syllabus: General Studies Paper-II (International Relations)
Source: TH
Context:
Recent statements by the Prime Minister highlight India’s deep reliance on major powers—China, Russia, and the United States—despite India’s rhetoric of strategic autonomy and multi-alignment. Understanding these dependencies is crucial for assessing India’s foreign policy and economic strategy.
Key Areas of Dependence
1. Dependence on the United States
- Trade and Markets: The US is India’s largest export destination, critical for industrial revenue.
- Education and Migration: Indian professionals dominate H-1B visas, with around 70% approvals in FY2023. The US remains a top choice for Indian students, and Green Cards are a long-term aspiration.
- Defense and Technology: India relies on US arms, engines for fighter jets, missiles, drones, and reconnaissance systems. Strategically, the US acts as a counterbalance to China in the Indo-Pacific.
2. Dependence on China
- Consumer and Industrial Goods: Chinese products dominate India’s electronics, mobile components, and household appliances.
- Pharmaceutical Inputs: China supplies APIs and precursor chemicals vital for India’s pharma sector.
- Critical Commodities and Technology: Rare earth metals, solar equipment (polysilicon, wafers), fertilizers, machinery, computers, and semiconductors are largely imported from China.
3. Dependence on Russia
- Defense Equipment: India has relied on Russian arms since the 1970s; 60–70% of Army, Navy, and Air Force equipment depends on Russia.
- Energy: Russian oil imports surged from 4% in 2022 to nearly 40% at peak, locking refineries into Russian supplies.
Impacts of Foreign Dependence
- Strategic Constraints: India must balance relations carefully—it cannot antagonize China, Russia, or the US without diplomatic costs.
- Technological Gaps: Dependence persists in engines, sensors, and semiconductors, despite policy measures.
- Slow Capacity Building: Developing domestic capabilities takes years; policies often lag behind strategic needs.
- Capital and Skill Shortages: R&D, infrastructure, and human capital gaps hinder self-reliance.
- External Pressures: Sanctions, trade barriers, or diplomatic pressure can impact India when dependence is high.
Measures to Reduce Dependence
- Make in India: Boost domestic manufacturing in defense, electronics, and infrastructure.
- Defense Production & Indigenisation: Indigenous defense production reached ₹1.27 lakh crore (FY 2023–24), with 14,000+ items indigenised.
- Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan: Promote self-reliance across sectors.
- Semiconductor & Nuclear Push: First Made-in-India semiconductor by 2025; private investment in nuclear energy encouraged.
- Critical Minerals Mission: 1,200 sites under exploration for energy and defense minerals.
- Energy Independence: Offshore exploration, green hydrogen, and solar expansion to reduce fuel import dependence.
- Strategic Autonomy: Multi-alignment policy balances global partnerships while preserving national interests.
- Operation Sindoor: Indigenous counter-terror operations signal technological independence.
- Indus Waters Treaty Reassessment: Strengthening control over water resources.
Policy Recommendations
- Revive Manufacturing: Prioritize a manufacturing revolution to match India’s GDP growth.
- Diversify Inputs: Reduce reliance on single-country suppliers for energy, minerals, and chemicals.
- Expand Exports: Broaden trade beyond the US to enhance economic independence.
- Unlock Domestic Potential: Encourage private and public sector entrepreneurship to build resilient supply chains and competitive industries.