France: Geography, Constitutional System and Strategic Partnership with India – A UPSC Synthesis
Syllabus: UPSC GS-I,II,&III (Geography, Diplomacy & Defence)
1. Introduction – Why France Matters for UPSC
France is one of Europe’s most influential states—geographically diverse, militarily powerful, and diplomatically central to the European Union and Indo-Pacific strategies. Located in Western Europe with coastlines on the Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea, English Channel, and North Sea, it enjoys exceptional maritime access.
Capital: Paris
System: Unitary semi-presidential republic
Global Status: UNSC Permanent Member, Nuclear Power
For UPSC, France is crucial because it links:
✔ European physical geography
✔ Nuclear energy & climate policy
✔ EU geopolitics
✔ Indo-Pacific security
✔ India–France strategic relations
PART I – PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY OF FRANCE
2. Physiographic Divisions
France exhibits classic European relief diversity.
(a) Plains & Basins
- Paris Basin, Aquitaine Basin
- Fertile soils → dense population and agriculture
(b) Central Massif
- Ancient volcanic plateau
- Remnant Hercynian mountains
- Pastoral farming & minerals
(c) Alps
- Young fold mountains
- Contains Mont Blanc – Western Europe’s highest peak
- Hydropower, glaciers, tourism
(d) Pyrenees
- Natural border with Spain
- Rugged relief, passes, pastoralism
(e) Jura & Vosges
- Medium-height forested ranges
3. Rivers & Climate
Major Rivers:
- Seine → English Channel
- Loire → Atlantic
- Garonne → Atlantic
- Rhône → Mediterranean (HEP, irrigation)
Climate Types:
- Oceanic west
- Continental east
- Mediterranean south
- Alpine highlands
Controlled by Atlantic westerlies, North Atlantic Drift, and mountain barriers.
4. Agriculture, Resources & Economy
France is the EU’s largest agricultural producer.
- Wheat, barley, sugar beet
- World-famous vineyards (Bordeaux, Champagne)
- Dairy in Normandy
Energy:
- Leader in nuclear power
- Hydropower (Alps/Pyrenees)
- Renewables expanding
Industries:
- Aerospace (Airbus)
- Defence manufacturing
- Luxury brands
- Tourism (world’s most visited)
Ports: Marseille, Le Havre.
PART II – POLITY & ADMINISTRATIVE STRUCTURE
5. Political System
- Semi-presidential republic
- Directly elected President
- Prime Minister handles domestic governance
- Bicameral legislature
Member of:
- EU, NATO
- G7
- OECD
- UN Security Council
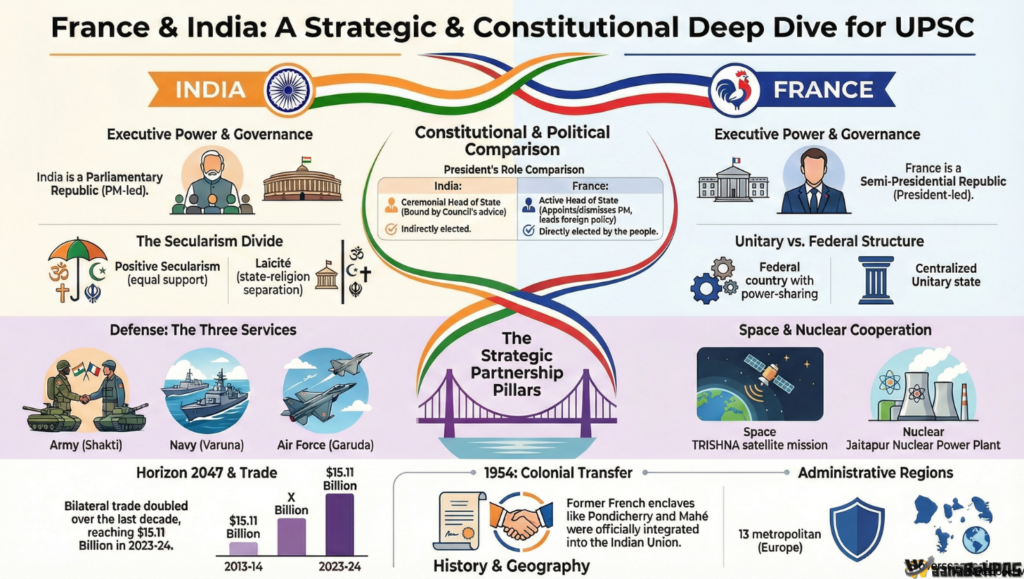
6. Administrative Geography
France has 18 regions:
13 Metropolitan Regions
Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, Île-de-France, Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur, Occitanie, Normandy, etc.
5 Overseas Regions
French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Mayotte, Réunion.
👉 These overseas territories make France a resident Indo-Pacific power, crucial for India’s maritime security calculus.
PART III – INDIA–FRANCE CONSTITUTIONAL COMPARISON
7. Constitutional Foundations
Both India and France operate under written constitutions built on republican ideals.
| Feature | India | France |
|---|---|---|
| System | Parliamentary Republic | Semi-Presidential |
| Head of State | Indirectly elected President | Directly elected President |
| Motto | Satyameva Jayate | Liberté, Égalité, Fraternité |
| Emergency | Arts 352-360 | Art 16 |
Value bridge: French revolutionary ideals inspired India’s constitutional philosophy—strengthening diplomatic trust.
8. Executive Models
India → Cabinet-led collective responsibility.
France → Strong presidency in foreign & defence policy.
France allows cohabitation; India ensures unified executive under PM.
👉 Strategic implication: France can act rapidly in crises; India emphasizes parliamentary legitimacy.
9. Judicial Structures
- India: Unified judiciary; Election Commission handles polls.
- France: Dual system—judicial + administrative courts; judiciary supervises elections.
Legal philosophies differ in rights enforcement—important for governance comparisons.
10. Secularism Models
India → Positive secularism (accommodation).
France → Laïcité (strict separation).
This difference shapes domestic politics and minority integration debates.
PART IV – INDIA–FRANCE STRATEGIC PARTNERSHIP
11. Historical Roots
Former French enclaves: Pondicherry, Karaikal, Yanam, Mahé, Chandernagore.
Transferred to India (1954–62).
Indian diaspora in France & Réunion strengthens people-to-people ties.
12. Horizon 2047 Roadmap
Marks 25 years of strategic partnership.
Key Pillars:
Defence: Rafales, Scorpene submarines → co-development engines.
Space: ISRO–CNES; climate satellites; Gaganyaan support.
Nuclear: Jaitapur plant; SMRs.
Digital: UPI integration in Paris.
👉 Reflects shift from buyer–seller to co-development, aligning with India’s Atmanirbhar Bharat.
13. Indo-Pacific Cooperation
France’s Indian Ocean territories give:
✔ Maritime Domain Awareness
✔ Joint patrols
✔ Naval exercises
✔ Logistics sharing
Conclusion – UPSC Takeaways
France illustrates:
✔ European physical geography
✔ Nuclear-driven energy security
✔ Semi-presidential governance
✔ Overseas strategic reach
✔ Deep Indo-Pacific partnership with India
For UPSC, France is a perfect case linking GS-I geography + GS-II diplomacy + GS-III energy & defence.











