Moon’s Sphere of Influence (MSI)
Subject: Science & Technology (UPSC Prelims, GS III)
Source: NIE
Context
ISRO has confirmed that the Chandrayaan-3 Propulsion Module (PM), while in its high-altitude Earth-bound orbit, briefly re-entered the Moon’s Sphere of Influence (MSI) and completed two lunar flybys.
What is the Moon’s Sphere of Influence (MSI)?
The Moon’s Sphere of Influence is the region around the Moon where the Moon’s gravitational force becomes stronger than Earth’s for the purpose of spacecraft navigation.
Inside this region, it is more accurate to treat a spacecraft as “orbiting the Moon,” even though Earth’s gravity is still present.
Location and Size
- MSI is an imaginary region around the Moon.
- It extends roughly 66,000 km from the Moon’s centre (approximate value used in mission planning).
- The actual shape is not a perfect sphere but an oblate spheroid.
How is MSI Estimated?
A simplified formula using the patched-conic approximation considers:
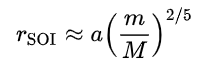
- Distance between Earth and Moon (~384,400 km)
- Mass of Earth
- Mass of Moon
Note: ISRO uses more accurate numerical simulations involving all major gravitational forces (Earth, Moon, Sun).
Features of the MSI
- Dominant gravitational control: Within MSI, the Moon’s gravity influences the spacecraft more than Earth’s.
- Not a physical boundary: It is a mathematical tool, not a real boundary in space.
- Two-body approximation: Helps switch calculations from Earth-centric to Moon-centric models.
- Earth and Sun still affect motion: Their gravitational pull continues to cause small perturbations.
Why is the MSI Significant?
1. Trajectory Planning
Space agencies use the MSI to decide when navigation models should shift from Earth-based to Moon-based calculations.
2. Lunar Orbit Insertion & Flybys
Accurate MSI boundaries help in timing braking manoeuvres, flybys, and orbit corrections.
3. Reducing Navigation Errors
It helps predict gravitational disturbances more reliably and ensures safe, efficient mission operations.