U.S. Imposes 25% Tariff on Indian Imports Amid Trade and Geopolitical Tensions
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus: International Relations, Indian Economy (Trade Policy) (UPSC GS II & III)
Context
Starting August 1, 2025, the U.S. government has imposed a 25% import tariff on Indian goods. The move is linked to ongoing trade disputes and India’s continued energy and defence engagement with Russia.
What Has Happened?
- The U.S. President has announced a 25% tariff on all eligible imports from India.
- Additional penalty duties have been added due to India’s continued oil and defence trade with Russia.
- This step is associated with the proposed Russia Sanctions Act 2025, which is under consideration in the U.S. Congress.
Why the Tariff Was Imposed
- Trade Imbalance: The U.S. aims to push India to reduce its own tariffs and non-tariff barriers.
- Russia Factor: The tariff serves as a warning against India’s trade ties with Russia amid the Ukraine war.
- Push for Trade Deal: The U.S. wants to fast-track a “fair and reciprocal” bilateral trade agreement with India.
Key Developments
- Strong Language Used: The U.S. President described India’s trade policies as “obnoxious,” highlighting high tariffs and regulatory opacity.
- Russia Sanctions Act 2025: This proposed law may allow the U.S. to impose up to 500% tariffs on countries trading oil with Russia.
- Talks Broke Down: The tariffs follow the fifth unsuccessful round of India-U.S. trade negotiations held in Washington.
- Earlier Tariffs Reinstated: A previously suspended 26% tariff (from April 2025) has now been reintroduced in a stricter form.
India’s Reaction
- The Ministry of Commerce has said it is reviewing the situation and remains committed to protecting its farmers, MSMEs, and entrepreneurs.
- India referred to its recent FTA with the UK as proof of its fair trade practices and global trade openness.
Implications for India
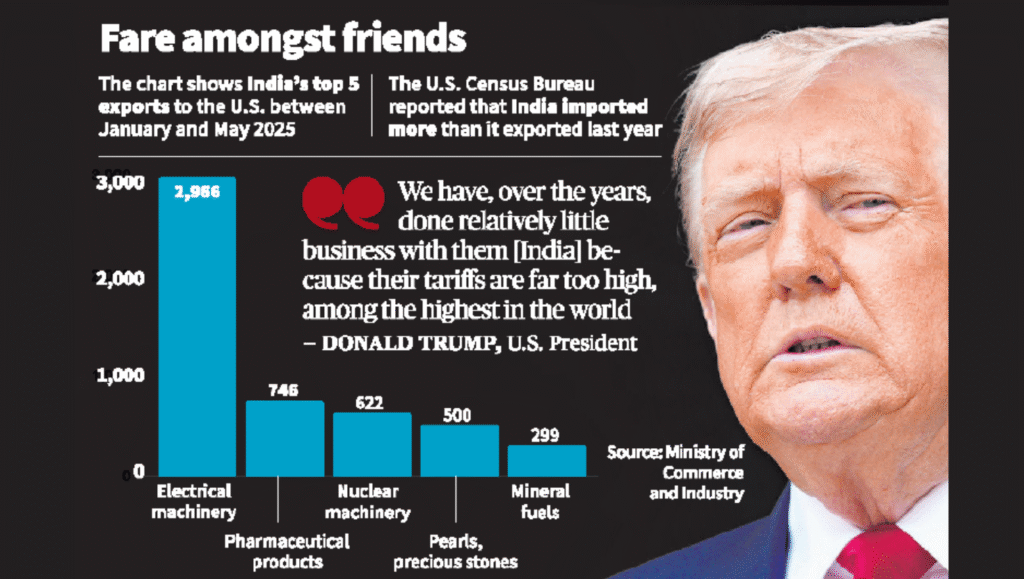
- Impact on Exports: Indian sectors such as textiles, pharmaceuticals, and engineering goods may become less competitive in the U.S. market.
- Strain on Bilateral Ties: The tariff could slow progress on a long-awaited India-U.S. trade agreement and weaken strategic cooperation in platforms like the Quad.
- Pressure on Strategic Autonomy: India’s multi-alignment foreign policy, particularly its Russia engagement, faces increased pressure from Western economic measures.