2025 Nobel Prize in Physics Awarded for Macroscopic Quantum Discoveries
Syllabus: Awards and Honours (UPSC Prelims)
Source: TOI
2025 Nobel Prize in Physics Awarded for Quantum Discoveries
Laureates:
- John Clarke – University of California, Berkeley
- Michel H. Devoret – Yale University and University of California, Santa Barbara
- John M. Martinis – University of California, Santa Barbara
They were awarded the 2025 Nobel Prize in Physics for their “discovery of macroscopic quantum mechanical tunnelling and energy quantisation in an electric circuit.” The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences noted that their experiments “revealed quantum physics in action” using chip-based electrical circuits, showing that quantum phenomena can occur on scales visible to the naked eye. This answered a key physics question: the maximum size at which quantum effects can manifest. Their work demonstrated that quantum behaviour is not limited to atomic or subatomic scales.
About the Experiments
- Timeline: Conducted in 1984–1985
- Setup: Electronic circuits made of superconductors separated by a thin insulating layer, known as Josephson junctions.
- Findings: When current passed through these circuits, all charged particles acted as if they were a single particle, spanning the entire system.
- Significance: This provided clear evidence of macroscopic quantum mechanical effects, a major breakthrough in understanding quantum systems.
Nobel Week Overview
- After the Physics Nobel, the Chemistry Nobel will be announced on Wednesday, Literature on Thursday, and the Peace Prize on Friday.
- The Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences will be announced on October 13.
- Recent Winners:
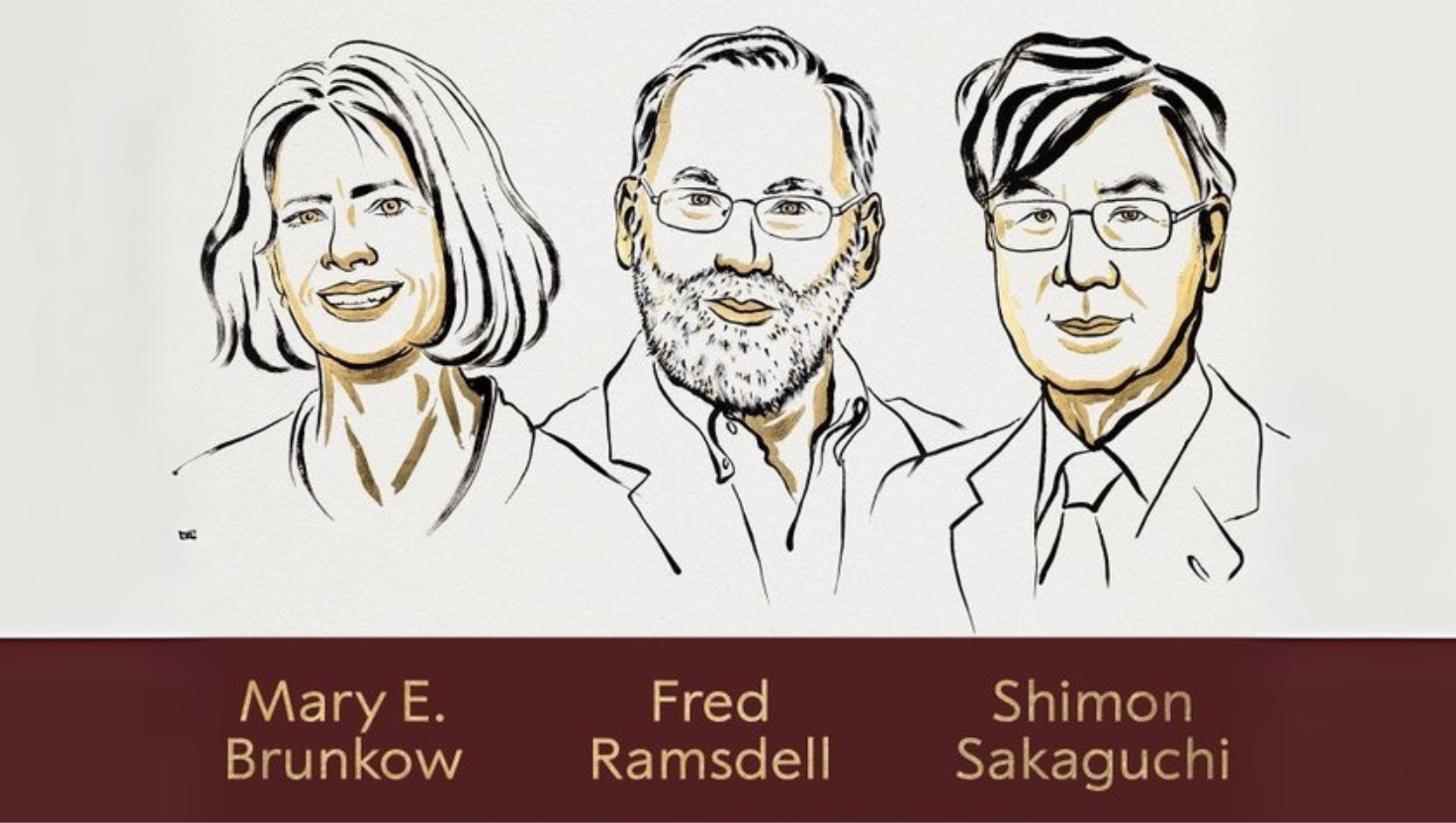
- Medicine 2025: Mary E. Brunkow, Fred Ramsdell, and Shimon Sakaguchi – for explaining how the immune system distinguishes between harmful invaders and body cells.
- 2024 AI Nobel: John Hopfield and Geoffrey Hinton – for foundational contributions to machine learning.
Nobel Prize Rewards
- Winners receive a gold medal, a diploma, and 11 million Swedish kronor (~$1 million).
- The award is presented by King Carl XVI Gustaf in Stockholm on December 10, Alfred Nobel’s death anniversary.
Selection Process
- Nominations: Sent by the Nobel Committee for Physics each September to qualified individuals, including Academy members, previous laureates, and senior professors.
- Deadline: January 31 for submissions; self-nominations are not allowed.
- Evaluation: Between March and May, external experts review nominations. A detailed report is submitted to the Academy in September.
- Final Selection: Conducted in early October through a majority vote.
- Confidentiality: All nominations remain sealed for 50 years.
Key Facts about the Physics Nobel
- Since 1901: 118 Physics Nobel Prizes awarded
- 47 to a single laureate
- 38 shared among three laureates
- Not awarded: Six years, mainly due to world wars
- Total laureates: 226, including icons like Albert Einstein, Marie Curie, Niels Bohr, Richard Feynman, and Peter Higgs
- The award recognises transformative discoveries that reshape humanity’s understanding of the universe.